Earth’s average temperature set a new unofficial record high on Thursday, the third such milestone in a week that already rated as the hottest on record and what one prominent scientist says could be the hottest in 120,000 years.
But it’s also a record with some legitimate scientific questions and caveats, so much so that the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has distanced itself from it. It’s grabbed global attention, even as the number—63 degrees Fahrenheit (17.23 degrees Celsius)—doesn’t look that hot because it averages temperatures from around the globe.
Still, scientists say the daily drumbeat of records—official or not—is a symptom of a larger problem where the precise digits aren’t as important as what’s causing them.
“Records grab attention, but we need to make sure to connect them with the things that actually matter,” climate scientist Friederike Otto of the Imperial College of London said in an email. “So I don’t think it’s crucial how ‘official’ the numbers are, what matters is that they are huge and dangerous and wouldn’t have happened without climate change.”
Thursday’s planetary average surpassed the 62.9-degree mark (17.18-degree mark) set Tuesday and equaled Wednesday, according to data from the University of Maine’s Climate Reanalyzer, a tool that uses satellite data and computer simulations to measure the world’s condition. Until Monday, no day had passed the 17-degree Celsius mark (62.6 degrees Fahrenheit) in the tool’s 44 years of records.
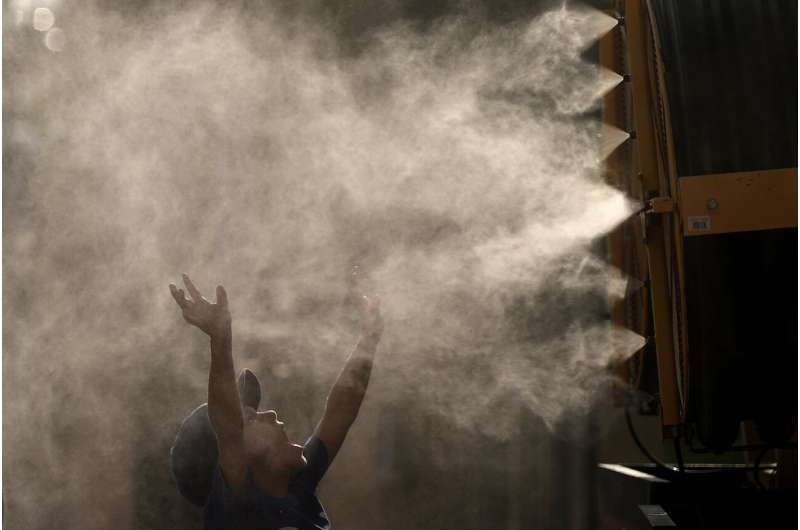
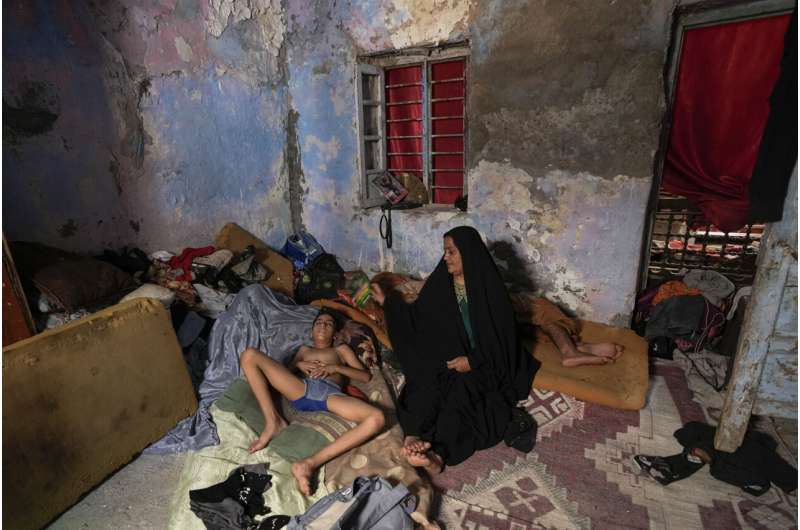
 A Iraqi woman fans her child during a power outage at their home in Baghdad, Iraq, Thursday, July, 6, 2023. Credit: AP Photo/Hadi Mizban
A Iraqi woman fans her child during a power outage at their home in Baghdad, Iraq, Thursday, July, 6, 2023. Credit: AP Photo/Hadi MizbanTemperatures were so brutally hot Thursday in Adrar, Algeria, that the overnight low dropped only to 103.3 degrees (39.6 degrees Celsius ). That was an all-time nighttime low for Africa, according to weather historian and climatologist Maximiliano Herrera.
The temperature is ramping up across Europe this week, too. Germany’s weather agency, DWD, has predicted highs of 37 degrees C (99 degrees F) on Sunday and the Health Ministry has issued a warning to vulnerable people.
While there are small spots of cooler-than-normal temperatures across the globe, the University of Maine measurement is an average. That means some places—including both polar regions—will be extraordinarily warmer than normal and others will be cooler. On average it’s about 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degree Celsius) warmer than the 1979-2000 average, which is warmer than the 20th and 19th century averages.
And 70% of the world is covered by oceans, which have been spiking record heat for months.
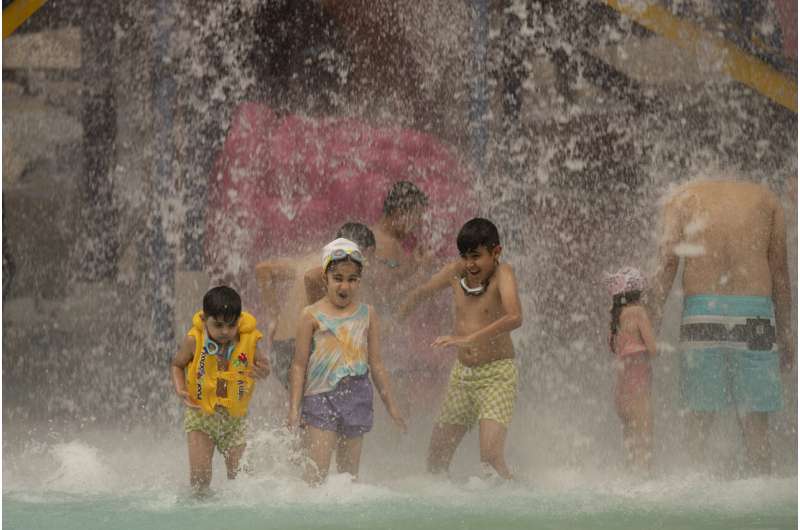 People escape the searing summer heat at Baghdad Aquatic Center in Baghdad, Iraq, Thursday, July, 6, 2023. Credit: AP Photo/Hadi Mizban
People escape the searing summer heat at Baghdad Aquatic Center in Baghdad, Iraq, Thursday, July, 6, 2023. Credit: AP Photo/Hadi MizbanScientists say the heat is driven by two factors: Long-term warming from greenhouse gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels and a natural El Nino warming of part of the Pacific that changes weather globally and makes an already warming world a bit hotter.
Now, the entire week that ended Thursday averaged that much.
“It is certainly plausible that the past couple days and past week were the warmest days globally in 120,000 years,” or at least 23,000 years, University of Pennsylvania climate scientist Michael Mann said, citing a 2021 study.
Climate scientist Zeke Hausfather of the tech company Stripe and Berkeley Earth temperature monitoring group said it’s clearly the hottest day since 1900, “very likely the warmest week in the past 2,000 years.” He said he wouldn’t be surprised if it is the warmest in 120,000 years but that relies on proxy measurements like tree rings which aren’t precise, so it’s harder to be confident.
Read more at : phys.org;
Photos: phys.org;

Leave a Reply